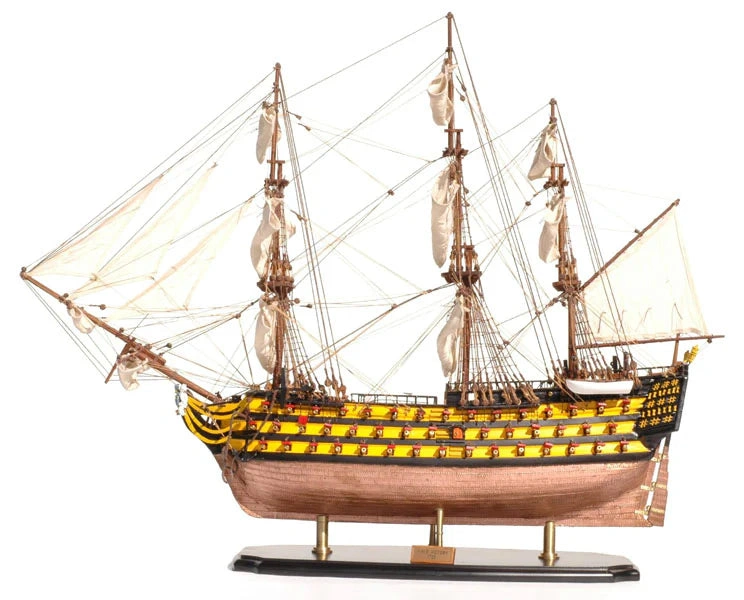
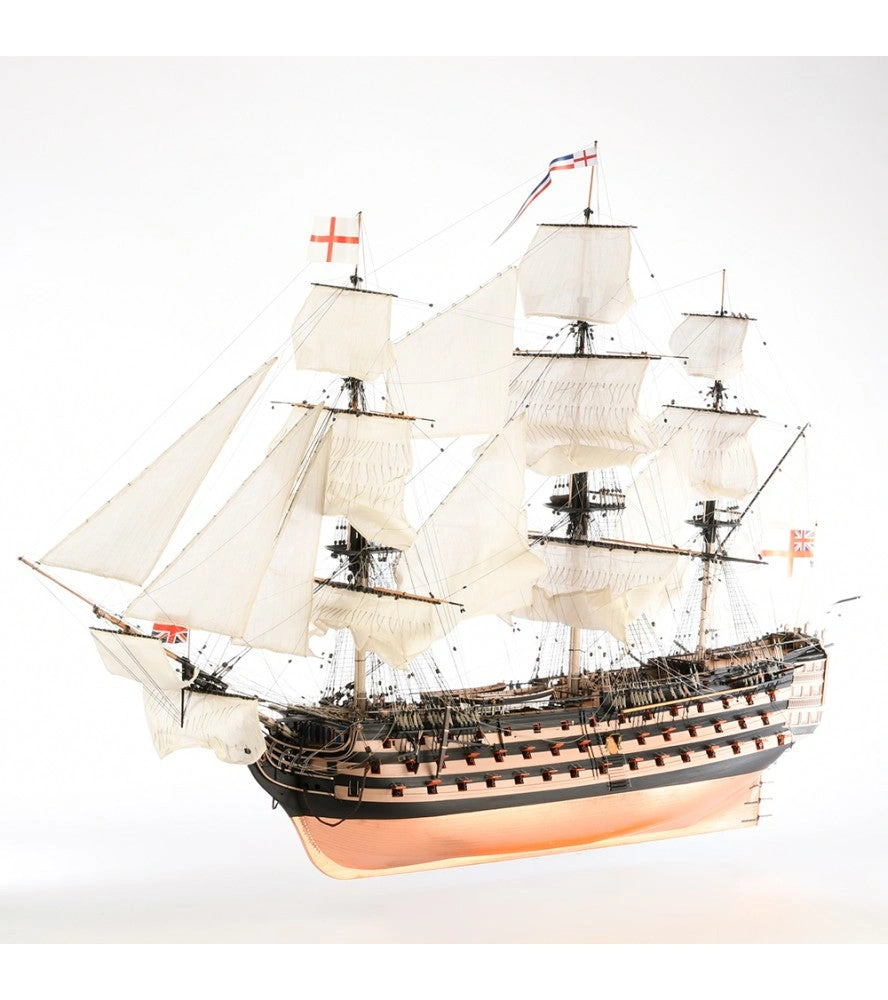
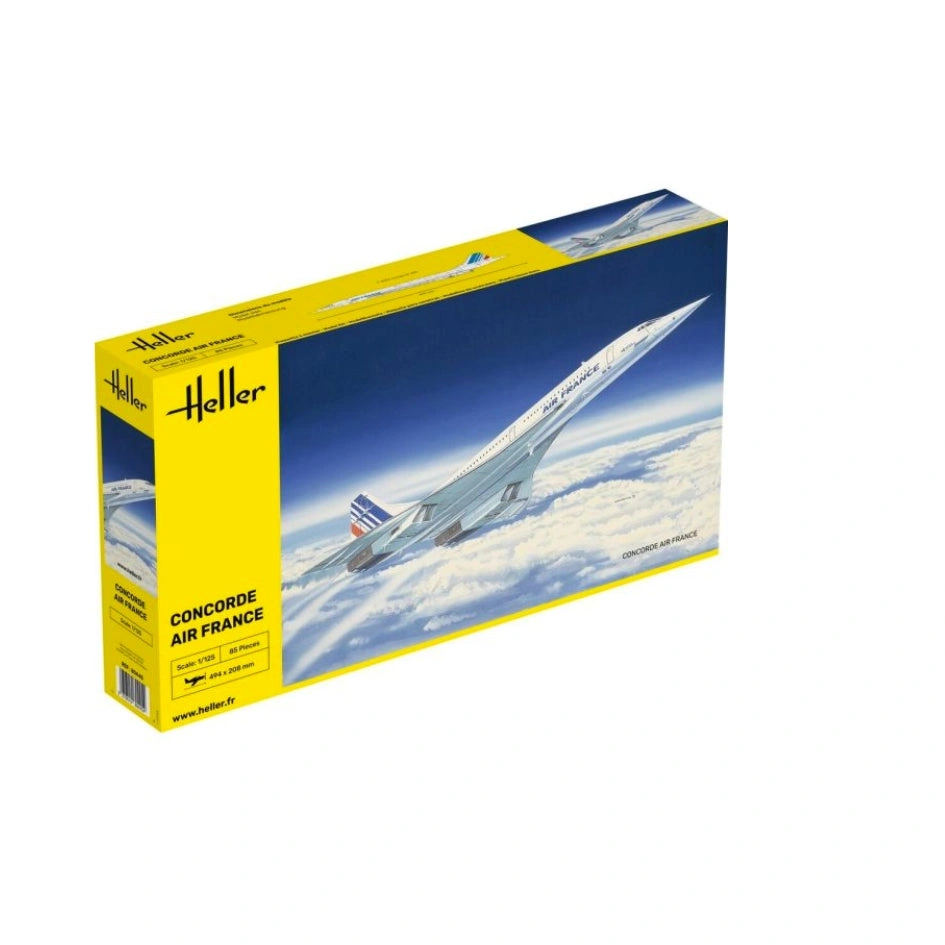
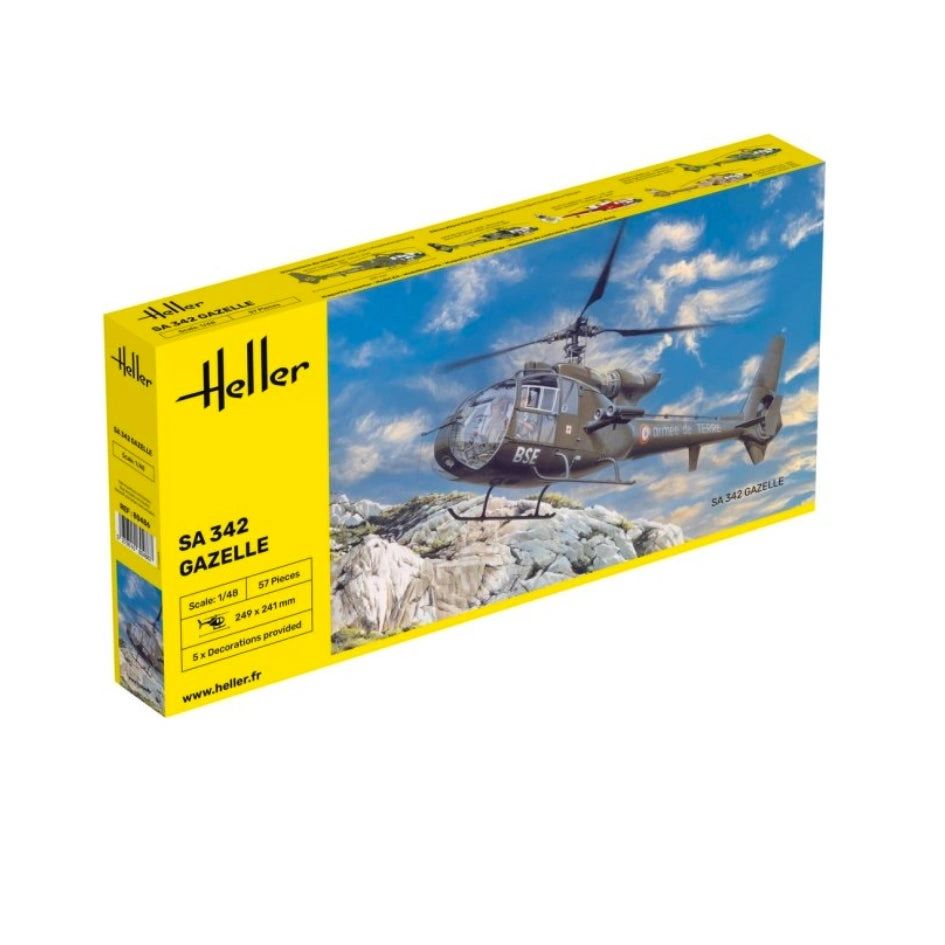
Plastic model of a ship for gluing. The set includes: glue, brush and basic paints.
HMS Victory was a sailing ship of the line of the British Navy, built between 1759 and 1765 at Chatham Dockyard. Her home port is Portsmouth, England.
The plans for the ship were ready in June 1759 and were based on the design of HMS Royal George, built at Woolwich Dockyard in 1756. The ship's chief designer was Sir Thomas Slade, who decided to use the newly constructed dry dock for the construction of large vessels. The ship's keel was laid down on 23 July 1759 in the Old Single Dock, and the name for the ship was chosen in October 1760, in memory of the British victories during the Seven Years' War at the Battle of Minden and the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, as well as the naval battles of Lagos and Quiberon Bay.
She was the fifth RN ship to bear the name Victory, the previous one having sunk in 1744[1] with all hands. After a short break, construction was completed on 7 May 1765. The cost of building was £63,176.3s, which is equivalent to £50 million in today's prices. The timber used in the construction was from 6,000 trees, 90% of which was oak.
The first years of the ship's service were spent in reserve, with dismasted masts, she lay for 13 years at the mouth of the Medway. In March 1778 John Lindsay was appointed as the ship's first commander. However, in May of the same year, Admiral Augustus Keppel raised the flag on the ship, and Rear Admiral John Campbell took over the command of the ship. At that time, the ship was armed with iron 32 and 42 pounder guns (30 guns), 30 24 pounder guns and 40 12 pounder guns. Two 68 pounder carronades were later added.
Under the command of Admiral Keppel, the ship took part in the First Battle of Ushant. Then, in March 1780, the ship underwent a refit, which consisted of lining the ship's bottom below the waterline with 3,923 sheets of copper sheeting, protecting the bottom from marine pests.
In December 1781, the ship, under the command of Commodore Henry Cromwell and the flag of Rear Admiral Richard Kempenfelt, took part in the Second Battle of Ushant.
In 1797, the ship, now under the command of Commodore Robert Calder and the flag of Admiral Sir John Jervis, took part in the Battle of Cape St. Vincent.